Testing beyond and for registration
Background
If you ask submitter what is most demanding part at preparation for product registration, you might hear testing. From the review of regulatory affairs, it is called also non-clinical test, bench test or performance testing. For developer, testing is derived from design input to be shown as evidence to design output. So it is equivalent to verification and validation (V&V). V&V is required at chapter 7.3.6 and 7.3.7 at ISO 13485.
Validation: Confirmation through provision of objective evidence that the requirements for a specific intended use or application have been fulfilled.
Verification: Confirmation by examination and provision of objective evidence that the specified requirements have been fulfilled.
For authority, testing is oft most important document under strict review, because it demonstrates efficacy, reliability, and safety of medical device. It is an evidence to be compliant with standards and essential requirement. Often the performance data on instruction for use or datasheet is to match with rational testing.
Testing to relevant standards (e.g. IEC 60601-1 series) shall be provided. However there are in many cases of company or lab own method.
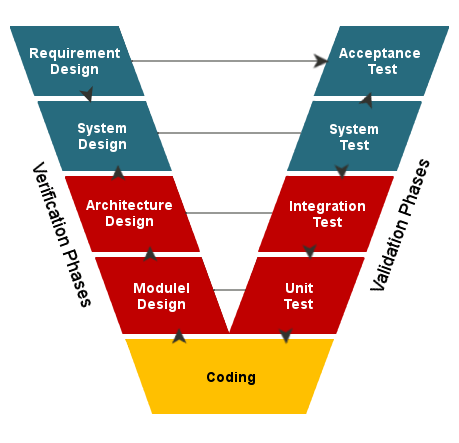
The testing at technical documentation to submit is only mini portion of all verification and validation , s. figure.
In term of test (Verification and Validation)
The typical tests are
· Chemical, physical
· Biocompatibility
· Software validation
· Electrical Safety and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
· Packaging, Stability and Shelf-Life
· Sterilization
· Microbiological
· Usability
International testing can be executed extra in local market as
· Type testing in China
· Usability testing in US
· Anatel testing in Brasil
· Wireless testing
*in this article we exclude the process validation, animal and clinical testing.
Testing is usually involved by many parties in -and out of company as
· Test engineer internal and external
· Test prover and releaser
· Technical supporter
· Regulatory affairs manager
· Risk manager
· Product manager
· Marketing manager
Don’t forget distributors or sales personals who use the performance data of test to make subject product competitive at tender and all other sales activities.
Testing can be related to technical documents:
· Risk management file
· Software file
· Verification and validation (plan and report)
· Design input, design output, design transfer
· Marketing material as IFU
Workflow of test (Verification and validation)
The workflow of test can be diverse depending with which tool manufacture records design control and where to conduct test. We just make a basic workflow as show case in this article.
1. Define user needs, specifications
Now we are in design stage. From user needs it deviates to design input and design out (specification). To verify the specification, a test is needed.
2. Search applicable standards
The best case for a normative reference is an internal standard. Otherwise for individual device, manufacturer or labs have to develop a solid test method.
3. Draft test plan with acceptance criteria
Found the method, the test plan should be written in detail with sample selection, test set up, test objectives and instrument and acceptance criteria. Prior to test, test protocol should be also prepared.
4. Plan test project if applicable
Ideally a project for a complex external test is beneficial. You have to apply for a test to get a slot in time. After contract a close discussion of test plan should be exchanged. The resources must be planned precisely. Don’t forget that the test could fail, think of plan B.
5. Execute the test
According the test plan and setting in protocol, a test is started. It will be accompanied with many rounds of trouble shooting. The output of test is adjusted and filled test plan and protocol. Note all anomalies and make picture or videos to remember critical working steps.
6. Evaluate the test
At the end the test should be evaluated by different experts. If the test data is too long, make different annexes as attachment after report. An evaluation helps reviewer later to examine the test, of course with a distinct “passed”.
For developer the specifications should be frozen depending on the design stage. All related documents as risk management, design control files, instruction for use, label should be updated.
Template of test plan, report and summary
All the parts of test are actually critical. Test plan should be prepared with rational and compliant with local or international standards. Test protocol should be consistent with plan and evaluation. Ultimately manufacturer should be able to evaluate the result with criteria.
Test is not unique done once. It should be repeated or revised in different life cycle of medical device. So the test records in general should be traceable, repeatable, understandable and conform.
Depending on where the test is performed, testing can be made of
- One report with plan, protocol and evaluation
- Test plan, test protocol and test evaluation
- External reports with annex, internal test summary
Be aware that you may and should repeat core parts of test in many test documents if divided to many different documents as objective, method, criteria, result and summary.
These below are often must have in test plan, protocol and evaluation:
Objective, applied standards, method, test sample selection, pass/fail criteria, result, evaluation discussion
Do you know ithat testing costs mostly during the product development and the test with bad quality raises later non-compliance in the field? The topic test is more than complex. The usual faults of test are:
- Non-compliance to standard
- No intelligent equivalent summary to avoid retest upon product change
- No enough qualification of external lab
- Bad communication with external lab
- No pro-active involvement of regulatory expert
- No checklist or template of testing
- No traceable matrix requirement and testing
- Testing report too technical to understand at authority
Contact us at any stage from concept development, V&V to technical documentation. We understand engineering, quality management and regulatory affairs.






